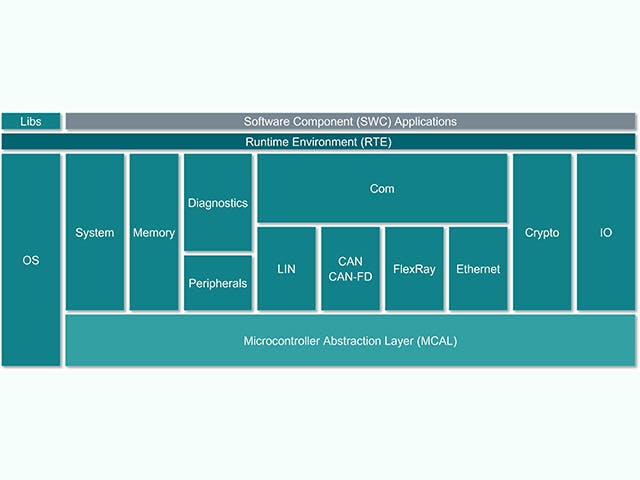
AUTOSAR embedded software platform
Embedded software teams need to rapidly and efficiently develop and deploy software for automotive ECUs to deliver in-vehicle features and functionality. AUTOSAR is the framework that enables this efficient development of embedded application software in the context of vehicle system development.
AUTOSAR embedded software platform
The Capital embedded portfolio, available supporting AUTOSAR R20-11 version of the standard, is scalable for use in low-power microcontrollers to multicore system-on-chips, running a combination of runtime and OS technologies.
Generative software configuration
The Capital Embedded AR Classic software enables accelerated correct-by-construction embedded software configuration using automation in an AUTOSAR-aware environment.
Software verification using virtual ECUs
Capital includes a unique virtual verification technology, which enables engineers to verify real-time AUTOSAR embedded software functionality before target silicon is available.