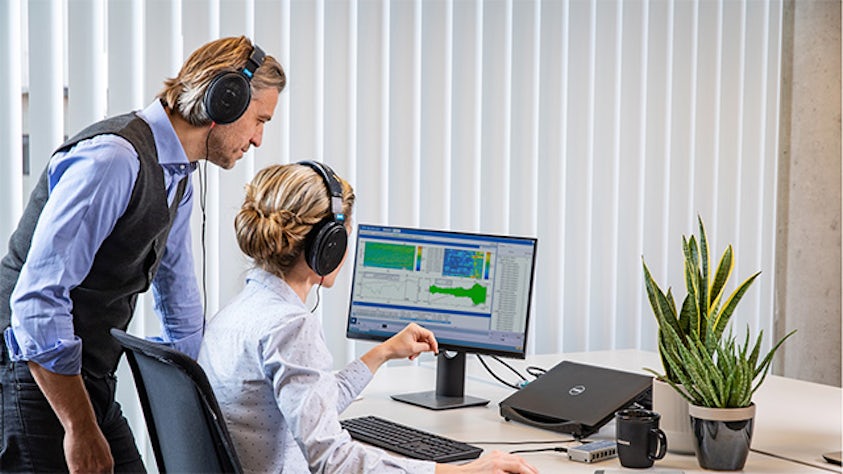
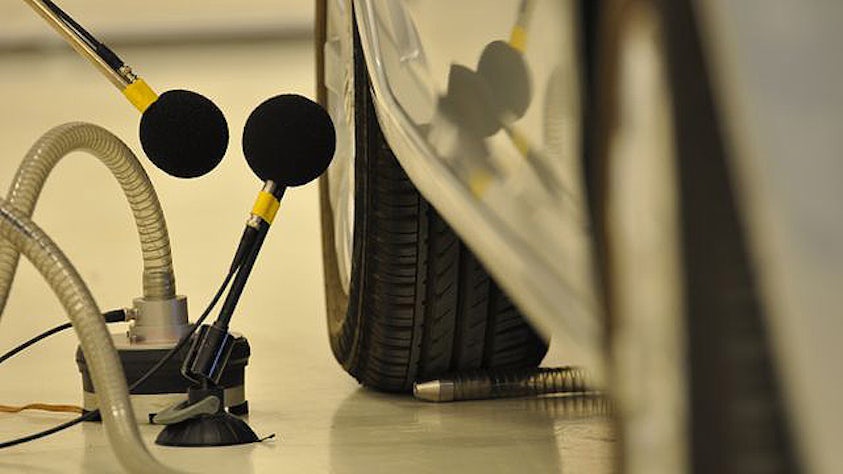
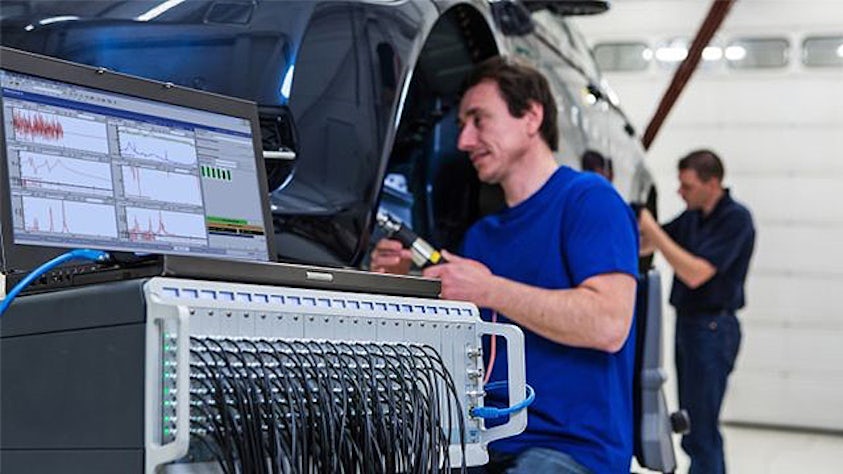
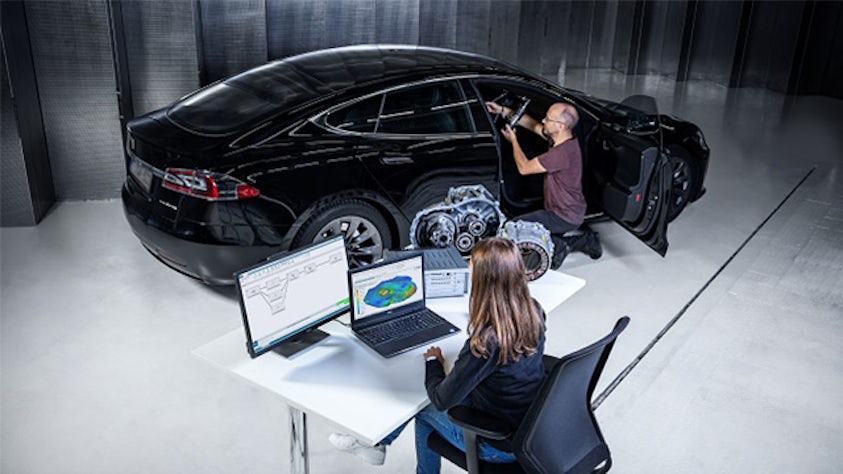
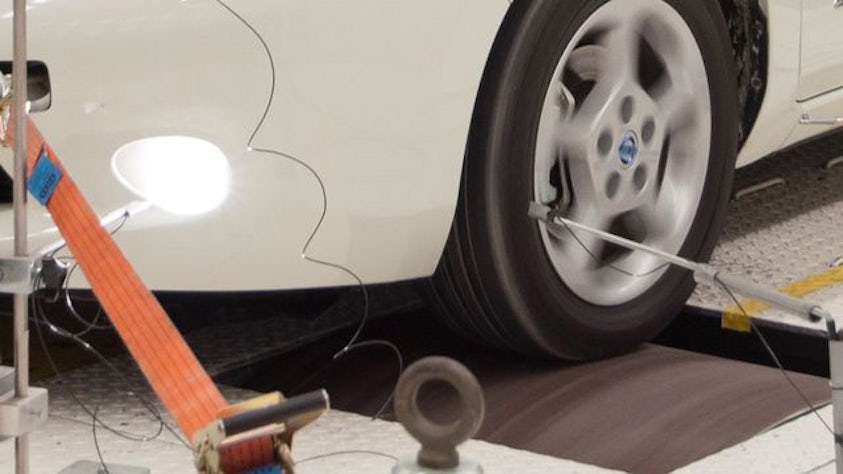
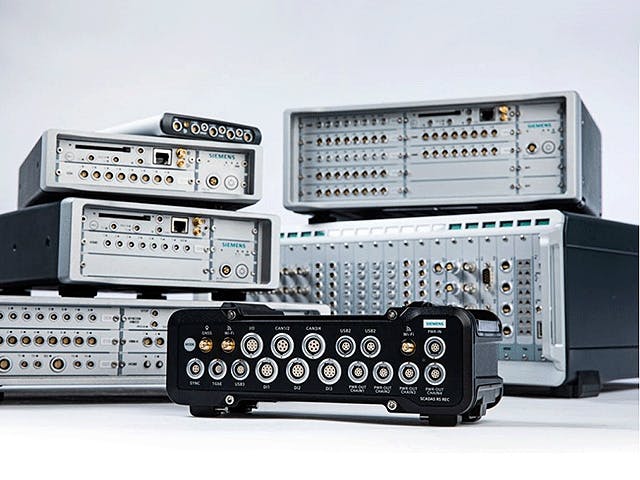
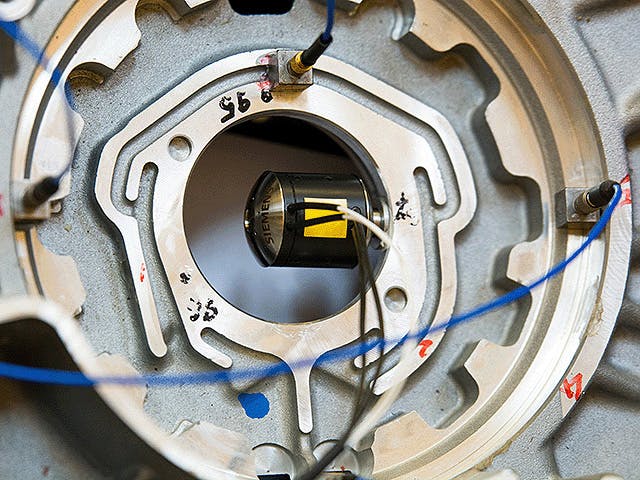
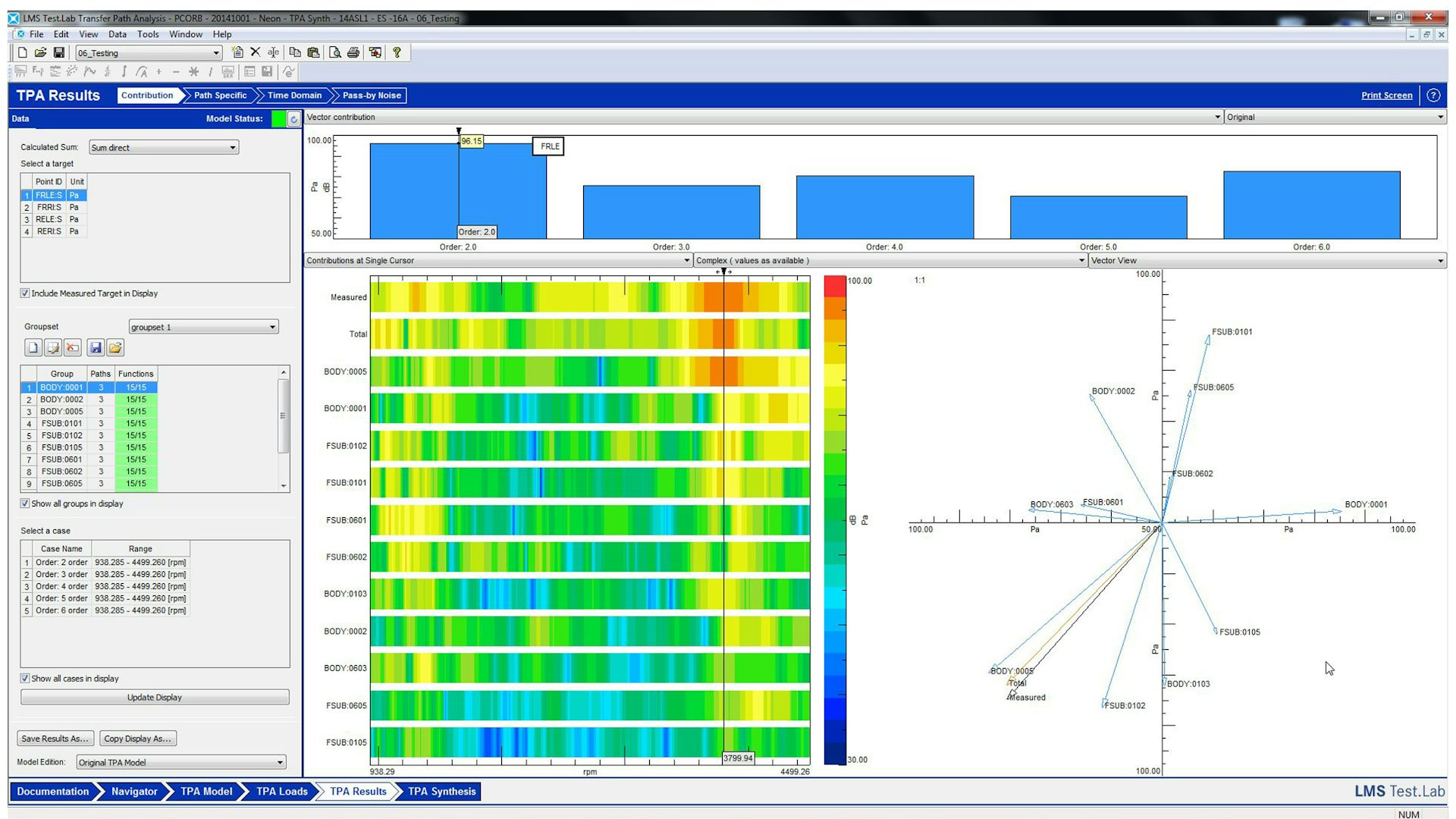
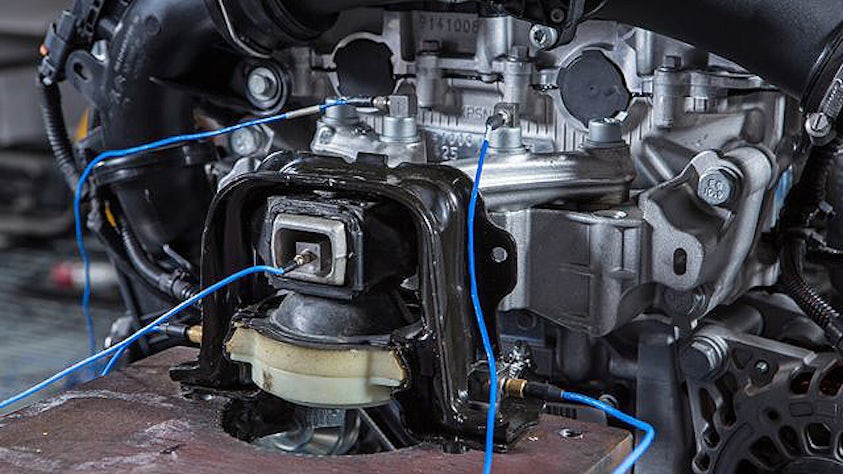
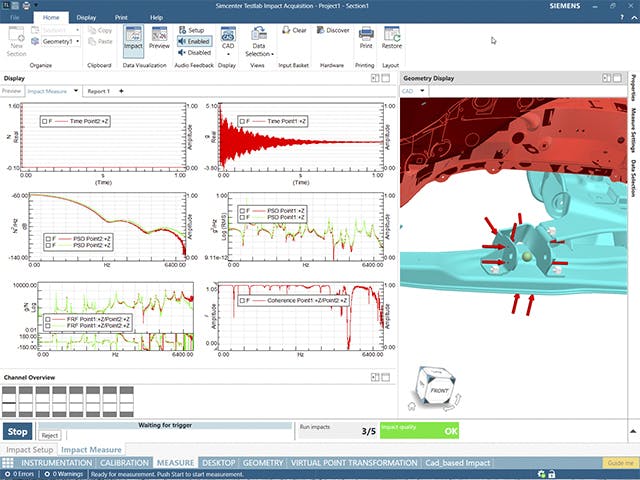
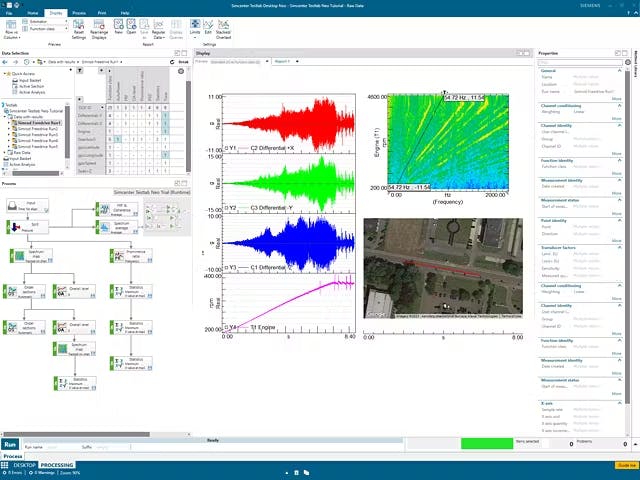
In order to fully understand the vibration behavior of a system, engineers perform a transfer path analysis (TPA) that helps them identify and assess structure-borne and airborne energy transfer routes, from the excitation source to a given receiver location.
Transfer path analysis quantifies the various sources and their paths and figures out which ones contribute the most to the noise issues and which ones cancel each other out. From the quantified and modeled sources and paths, it becomes a relatively straightforward design task to optimize vibro-acoustic and the noise, vibration, and harshness (NVH) performance of the system.